Navigating the Importance of CAGR in Financial Analysis
May 19, 2024 By Susan Kelly
Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) is a very important number in finance, and it's used to show the mean yearly growth rate of an investment over a certain period that is more than one year. By taking into account fluctuations, CAGR helps in making comparisons easier by giving an average rate of increase each year. This article will talk about what CAGR means, how you can calculate it, why this number matters so much for understanding investments better along many different uses within finance analysis.
What is the Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR)?
The geometric progression ratio, which is called Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR), gives a constant rate of return over time. It gets popular because it shows an evened-out yearly growth percentage that balances out the instability and ups and downs seen in year-to-year growth ratios. Concentrating on CAGR allows investors and analysts to compare growth percentages of various investments or financial tools more precisely.
CAGR is useful for understanding the real growth rate of an investment because it gives a smooth growth rate over time. When you use simple calculations to find out how much something has grown or shrunk, these could make short-term gains and losses appear bigger than they are. However, CAGR shows a steady yearly return which makes it more dependable to assess the performance of different investments in longer timeframes. This makes CAGR a better tool for comparing the growth rates of assets that have varying levels of volatility.
- Consistency: CAGR provides a consistent growth rate, essential for long-term financial planning.
- Comparability: Useful for comparing investments with varying durations and volatility.
Calculating the CAGR
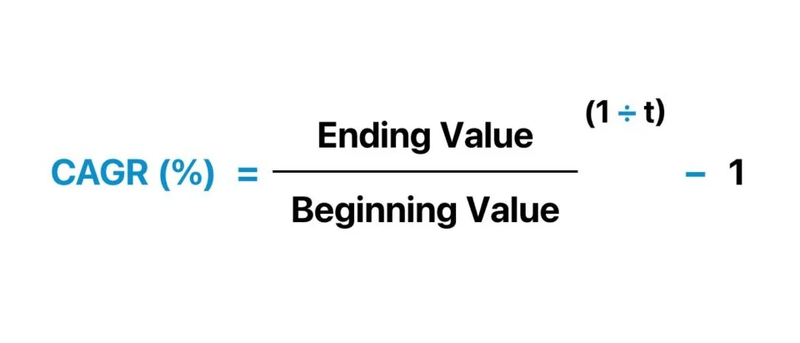
The formula for calculating CAGR is as follows:
CAGR=()11
where:
- EV is the ending value of the investment.
- BV is the beginning value of the investment.
- n is the number of years.
For CAGR, people who invest must know the very first and last values of their investment along with how long period it is growing. This formula helps to change these numbers into an annual rate which we can compare with other things. We should take care that the values put into this equation are exact so there's no misunderstanding about growth speed.
- Precision: Accurate initial and final values are crucial for correct CAGR calculation.
- Period Length: The length of the period significantly influences the CAGR outcome.
Significance of CAGR in Investment Analysis
CAGR is very useful for investors because it gives them a simple method to compare the growth rates of various investments. CAGR, unlike plain averages, considers compounding effects which give an accurate picture of how much an investment has grown over some time. It helps in comparing the past returns of stocks, mutual funds, and portfolios. Additionally, CAGR can be used to set investment goals and measure progress towards them.
Additionally, CAGR is useful for evaluating the value of investments over a longer period, as it provides an understanding of how performance might happen in the future based on past data. This characteristic turns CAGR into an important part of making choices for people who invest and want to balance their risk with rewards they can get from their portfolio. When you comprehend CAGR, it becomes easier to plan out your asset distribution and investment schemes.
- Investment Goals: Useful in setting and measuring progress towards investment objectives.
- Risk Management: Assists in balancing risk and reward by providing historical growth insights.
Applications of CAGR in Finance
CAGR is useful in many aspects of financial analysis, such as Investment Performance. It's used for evaluating and comparing the past performance of various investments. Financial Forecasting predicts future values of investments or financial metrics using historical data. Business Growth examines how quickly a company's revenue, profit, or other key performance indicators have grown over time. Comparative Analysis compares an investment's performance to industry norms or another similar investment.
Furthermore, CAGR is employed for assessing the performance of particular sectors or industries. This happens by comparing their average growth rates during a given period. Such comparison aids in recognizing which parts are experiencing constant growth and those that are falling behind, assisting with knowledgeable investment choices. It also proves beneficial when evaluating management strategies within companies across periods.
- Sector Analysis: Evaluate and compare the growth rates of different industries.
- Management Effectiveness: Measures the impact of management strategies on company growth.
Limitations of CAGR
Notwithstanding its application, CAGR has some boundaries. It supposes a steady growth rate that might not correspond to the actual situation in reality where growth rates can differ. Also, CAGR does not take into consideration the danger or instability linked with this investment. Investors need to look at CAGR in addition to other measurements for a full assessment of how well an investment has performed.
Another restriction is that CAGR might mislead by showing a stable growth rate in highly changeable markets. Because CAGR smooths out ups and downs, it could hide times of big declines or surges which may cause too hopeful or careful investment choices. So, while CAGR is very important, we should not trust only on it only for investment analysis.
- Volatility: CAGR can mask significant market fluctuations and volatility.
- Supplementary Metrics: Always use CAGR in conjunction with other financial metrics.
Real-world Examples of CAGR Calculation
To illustrate the calculation of CAGR, consider an investment that grows from $1,000 to $2,000 over five years. Using the CAGR formula:
CAGR=(20001000)151=(2)1510.1487 or 14.87%
This example shows that the investment grew at an average annual rate of 14.87% over five years.
Another example might be comparing the CAGR of two separate investments in the same time frame. For instance, let's say Investment A grows from $5,000 to $10,000 and Investment B grows from $3,000 to $7,000 over ten years. By calculating the CAGR for each one we can understand which investment had a better annual growth rate. This helps in selecting investments with more knowledge behind them.
- Multiple Investments: Comparing CAGR across different investments aids decision-making.
- Investment Duration: The period considered can significantly influence the CAGR result.
Comparing CAGR with Other Growth Metrics
Though CAGR is very useful, it's important to comprehend how it relates to other growth measurements such as simple annual growth rate (AGR) and internal rate of return (IRR). AGR offers a clear value for yearly growth, yet it doesn't consider compounding which makes its use less precise in analyzing long-term increase. IRR, alternatively, takes into account the time worth of money and can manage varying rates of growth but is more complex to compute. So, every metric is important in financial analysis. CAGR has its advantages because it's easy to understand and can ease the impact of volatility.
In addition, recognizing these differences aids in choosing the right measurement for different analysis intentions. For example, AGR may be better suited for evaluating growth in the short term while IRR is more suitable for projects with varying cash flows. By understanding the strong and weak points of each metric, investors can utilize them together to get a full understanding of their investments.
- Metric Suitability: Different growth metrics are suitable for different analytical purposes.
- Complementary Use: Using multiple metrics together provides a fuller investment analysis.
Conclusion
To sum up, it is very important for correct investment analysis and financial planning to comprehend and apply the Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR). When we understand how to calculate it, why it matters, and where we can use this rate, then investors will be able to make decisions with more knowledge and set growth goals that are possible.





